
Makrosites
Suas ideias em realidade digital!
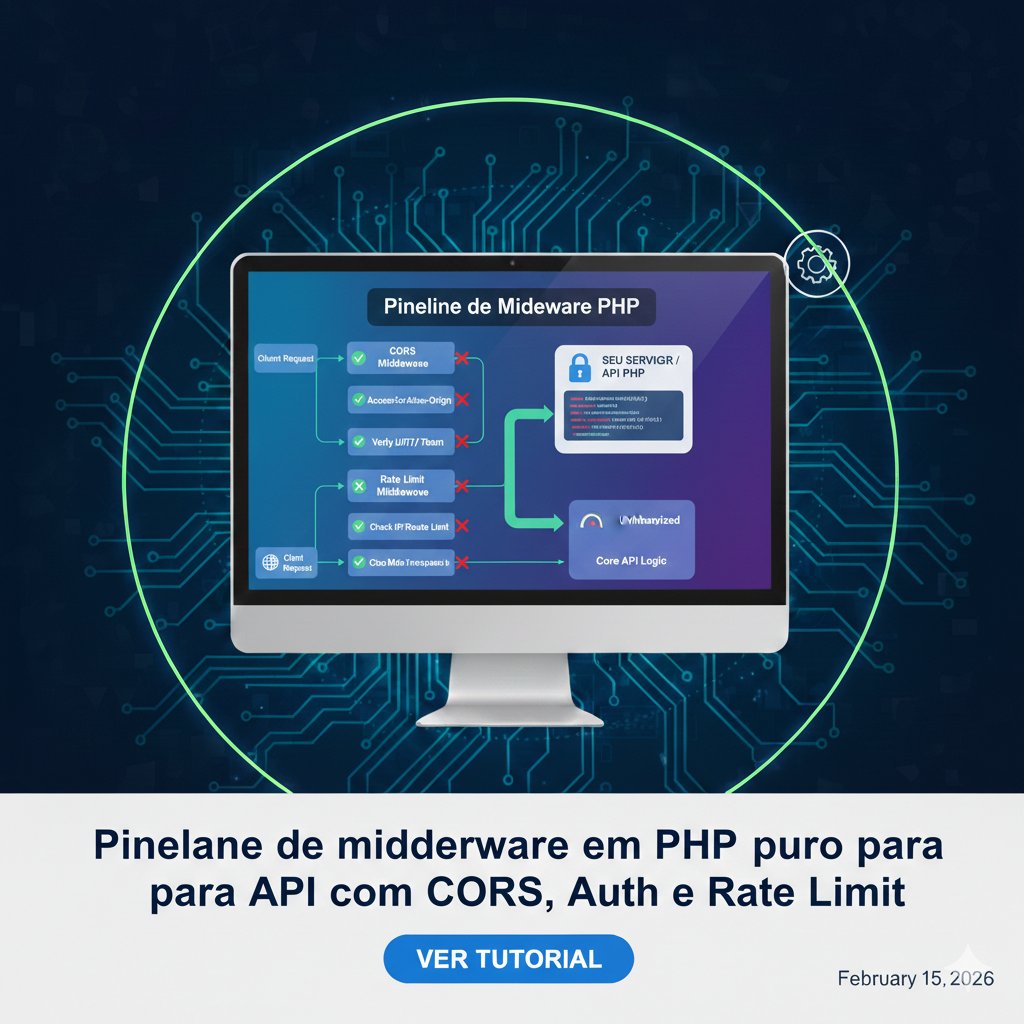
O que é Middleware (e por que você vai querer isso em PHP puro)?
Middleware é uma camada que roda antes (e às vezes depois) do seu controller. Ele serve para centralizar regras repetidas como:
- CORS
- JSON headers
- Autenticação (Bearer/JWT)
- Rate limit
- Logs
- Tratamento de erro
Sem middleware, você acaba copiando o mesmo código em todos os endpoints. Com middleware, você cria um pipeline (cadeia) e reaproveita.
Estrutura simples (recomendada)
/public/api/index.php
/src/Core/Router.php
/src/Core/Response.php
/src/Core/Request.php
/src/Middleware/MiddlewareInterface.php
/src/Middleware/MiddlewareQueue.php
/src/Middleware/JsonMiddleware.php
/src/Middleware/CorsMiddleware.php
/src/Middleware/AuthMiddleware.php
/src/Middleware/RateLimitMiddleware.php
/src/Controllers/...
1) Request e Response (bem básicos)
Request.php
<?php
class Request {
public string $method;
public string $path;
public array $headers;
public array $query;
public array $params = [];
public mixed $body = null;
public string $ip;
public function __construct() {
$this->method = $_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] ?? 'GET';
$this->path = parse_url($_SERVER['REQUEST_URI'] ?? '/', PHP_URL_PATH) ?: '/';
$this->headers = $this->readHeaders();
$this->query = $_GET ?? [];
$this->ip = $_SERVER['REMOTE_ADDR'] ?? '0.0.0.0';
}
private function readHeaders(): array {
$h = [];
foreach ($_SERVER as $k => $v) {
if (str_starts_with($k, 'HTTP_')) {
$name = str_replace('_', '-', strtolower(substr($k, 5)));
$h[$name] = $v;
}
}
// Authorization às vezes vem em outro server var
if (!isset($h['authorization']) && isset($_SERVER['REDIRECT_HTTP_AUTHORIZATION'])) {
$h['authorization'] = $_SERVER['REDIRECT_HTTP_AUTHORIZATION'];
}
return $h;
}
public function json(): array {
if ($this->body !== null) return (array)$this->body;
$raw = file_get_contents('php://input');
$data = json_decode($raw ?: '', true);
$this->body = is_array($data) ? $data : [];
return $this->body;
}
public function header(string $name, string $default = ''): string {
$key = strtolower($name);
return $this->headers[$key] ?? $default;
}
}
Response.php
<?php
class Response {
public static function json($data, int $code = 200): void {
http_response_code($code);
header('Content-Type: application/json; charset=UTF-8');
echo json_encode($data, JSON_UNESCAPED_UNICODE | JSON_UNESCAPED_SLASHES);
exit;
}
public static function error(string $message, int $code = 400, $details = null): void {
$payload = ['error' => $message];
if ($details !== null) $payload['details'] = $details;
self::json($payload, $code);
}
}
2) Interface de Middleware
Um middleware recebe o Request e um $next (próximo passo do pipeline).
<?php
interface MiddlewareInterface {
public function handle(Request $req, callable $next);
}
3) MiddlewareQueue (pipeline)
Este é o motor que executa a cadeia.
<?php
class MiddlewareQueue {
/** @var MiddlewareInterface[] */
private array $stack;
public function __construct(array $stack) {
$this->stack = $stack;
}
public function run(Request $req, callable $finalHandler) {
$runner = array_reduce(
array_reverse($this->stack),
function($next, $mw) {
return function(Request $req) use ($mw, $next) {
return $mw->handle($req, $next);
};
},
$finalHandler
);
return $runner($req);
}
}
4) Middlewares prontos (os mais úteis)
4.1) JsonMiddleware (garante JSON em tudo)
<?php
class JsonMiddleware implements MiddlewareInterface {
public function handle(Request $req, callable $next) {
header('Content-Type: application/json; charset=UTF-8');
return $next($req);
}
}
4.2) CorsMiddleware (com preflight OPTIONS)
<?php
class CorsMiddleware implements MiddlewareInterface {
public function __construct(private string $origin = '*') {}
public function handle(Request $req, callable $next) {
header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin: {$this->origin}");
header("Access-Control-Allow-Methods: GET,POST,PUT,DELETE,OPTIONS");
header("Access-Control-Allow-Headers: Content-Type, Authorization");
header("Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true");
if ($req->method === 'OPTIONS') {
http_response_code(200);
exit;
}
return $next($req);
}
}
4.3) AuthMiddleware (Bearer/JWT) aplicado só em rotas protegidas
Você pode aplicar em um grupo de rotas ou individualmente. Aqui vai uma versão simples que exige Bearer em certas rotas.
<?php
class AuthMiddleware implements MiddlewareInterface {
public function __construct(private array $protectedPrefixes = ['/api/private', '/api/posts']) {}
public function handle(Request $req, callable $next) {
// se rota não é protegida, passa
foreach ($this->protectedPrefixes as $p) {
if (str_starts_with($req->path, $p)) {
return $this->check($req, $next);
}
}
return $next($req);
}
private function check(Request $req, callable $next) {
$auth = $req->header('authorization', '');
if (!preg_match('/Bearer\\s+(.*)$/i', $auth, $m)) {
Response::error('Unauthorized', 401);
}
$token = trim($m[1]);
// Aqui você valida JWT ou token no banco:
// $payload = validateJWT($token, 'SEGREDO');
// if (!$payload) Response::error('Token inválido', 401);
return $next($req);
}
}
4.4) RateLimitMiddleware (por rota + IP)
Versão simplificada (você pode ligar na sua implementação Redis/MySQL do post anterior).
<?php
class RateLimitMiddleware implements MiddlewareInterface {
public function __construct(private array $rules = []) {}
public function handle(Request $req, callable $next) {
$routeKey = $req->path;
$ip = $req->ip;
$rule = $this->rules[$routeKey] ?? ['max' => 120, 'window' => 60];
// Aqui você chama rateLimitRedis(...) ou rateLimitMySQL(...)
// $r = rateLimitRedis($redis, $routeKey, $ip, $rule['max'], $rule['window']);
// Exemplo fake:
$r = ['allowed' => true, 'remaining' => 999, 'retry_after' => 0];
header("X-RateLimit-Remaining: {$r['remaining']}");
if (!$r['allowed']) {
http_response_code(429);
header("Retry-After: {$r['retry_after']}");
echo json_encode(['error' => 'Too Many Requests', 'retry_after' => $r['retry_after']]);
exit;
}
return $next($req);
}
}
5) Integrando tudo no index.php da API
No seu /public/api/index.php, você cria o Request, roda o pipeline e por fim chama o router/controller.
<?php
require_once __DIR__ . '/../../src/Core/Request.php';
require_once __DIR__ . '/../../src/Core/Response.php';
require_once __DIR__ . '/../../src/Core/Router.php';
require_once __DIR__ . '/../../src/Middleware/MiddlewareInterface.php';
require_once __DIR__ . '/../../src/Middleware/MiddlewareQueue.php';
require_once __DIR__ . '/../../src/Middleware/JsonMiddleware.php';
require_once __DIR__ . '/../../src/Middleware/CorsMiddleware.php';
require_once __DIR__ . '/../../src/Middleware/AuthMiddleware.php';
require_once __DIR__ . '/../../src/Middleware/RateLimitMiddleware.php';
$req = new Request();
$middlewares = [
new JsonMiddleware(),
new CorsMiddleware('https://www.makrosites.com.br'),
new RateLimitMiddleware([
'/api/auth/login' => ['max' => 5, 'window' => 60],
'/api/auth/refresh' => ['max' => 20, 'window' => 3600],
]),
new AuthMiddleware(['/api/posts', '/api/private']),
];
$queue = new MiddlewareQueue($middlewares);
$queue->run($req, function(Request $req) {
$router = new Router();
// registre rotas...
// $router->get('/api/health', fn() => Response::json(['ok' => true]));
$router->dispatch($req->method, $req->path);
});
Boas práticas (pra não virar bagunça)
- Middleware deve ser pequeno e focado (uma responsabilidade)
- Evite colocar regra de negócio em middleware
- Use prefixos de rotas protegidas
- Centralize headers CORS/JSON
- Padronize erro e resposta